Carlisle: St Cuthbert Without
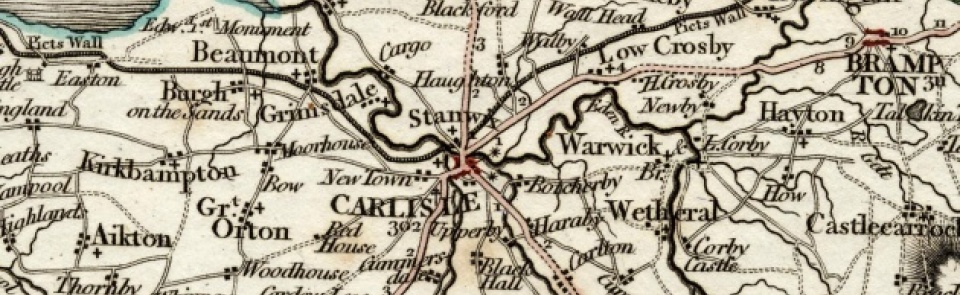
CP in St Cuthbert’s parish, Carlisle, Cumberland ward, Cumberland, comprising townships of High and Low Blackwell, Botcherby, Brisco, Carleton, Harraby, and Upperby. Carlisle city boundary extended 1887 and 1894, resulting in some loss of territory; Botcherby, Harraby and Upperby lost when city boundaries extended again 1912. CP absorbed Wreay CP (q.v.) 1934. This entry treats St Cuthbert Without CP as it existed between 1894 and 1912 and is arranged by constituent townships.
Acreage:
8,522 acres [3,449 ha] before boundary changes. Commons and waste grounds totalling 1,673 acres [677 ha] in Carleton, Brisco (and Wreay, in St Mary’s parish, Carlisle) within manor of Botchergate enclosed 1778.
Population:
1,039 in 1801, rising steadily to 1,872 in 1861 (last census year for which population of constituent townships is recorded separately). BLACKWELL (or Blackhall). Acreage: Blackwell High township: 2,563 acres [1,037 ha]; Blackwell Low township: 974 acres [394 ha]. Blackhall commons (described 1688 as narrow, barren and of little use other than for turbary) enclosed 1697.
Landownership:
manor of Blackwell granted by Henry I to Odard de Logis, whose descendants took surname de Wigton. Margaret de Wigton (1293-1349) granted it 1334 to Robert Parving. Sold to William Stapleton who sold it 1429-30 to Dacres, through which family it descended until sold 1716 to Sir Christopher Musgrave of Edenhall, remaining with that family to 20th century. Economy: agricultural until 20th century; Carlisle race course opened 1904 (replacing former course at The Swifts).
Places of worship:
Wesleyan Methodist chapel at Stoneraise built 1891; closed c.2010.
Schools and other institutions:
bequests to school at Blackwell 1785 and 1798; Durdar school at Stoneraise built by 1862; rebuilt 1871; now Stoneraise Primary School. BOTCHERBY. Acreage: 514 acres [208 ha]. Landownership: manor of Botcherby granted to Guy the hunter early 12th century, descending through his heirs, who took surname de Botcherby, to mid-13th century; later descent unclear. Economy: agricultural until 20th century; housing development since c.1930. Laundry near Botcherby Bridge, late 19th century. Places of worship: St Andrew’s mission church built 1890. Schools and other institutions: Board school built 1899; closed mid-1920s; re-opened 1939; converted to community centre. St Joseph’s Home for elderly (with chapel attached) built 1892; closed 1977; destroyed by fire 2002. BRISCO. Acreage: 1,956 acres [792 ha]. Landownership: part of manor of Botchergate, held by Carlisle Priory, passing to Dean and Chapter of Carlisle at Dissolution. Economy: largely agricultural; quarrying (notably at Newbiggin Quarry) later 19th century. Calico print works established before 1797; converted to iron works for making engines 1846; bought by Cowans Sheldon who moved to St Nicholas works (see Carlisle) later 19th century. Places of worship: none. Schools and other institutions: none. CARLETON. Acreage: 1,448 acres [586 ha], including part of Wragmire Moss, enclosed 1854. Landownership: see Brisco. Economy: largely agricultural; brick and tile works at Scalesceugh mid-19th century. Places of worship: chapel of Garlands Hospital opened 1875; closed 1997. Schools and other institutions: bequest to schoolmasters in Brisco, Carleton and Harraby 1785; in 1860 only Carleton had school; new school built 1872; closed 1984. Garlands mental hospital, built as Cumberland and Westmorland Lunatic Asylum, opened 1862; closed 1999 and site redeveloped for housing; replaced by Carleton Clinic. HARRABY. Acreage: 616 acres [249 ha]. Landownership: see Brisco. Economy: skinnery in 19th century. Lakeland laundry established 1935. Major expansion of housing 1948 to 1955 and later. Industrial estates from later 20th century. Places of worship: Harraby Methodist church opened 1948; closed 2009. Mission hall c.1954, replaced by St Elisabeth’s church, built 1966-7. Roman Catholic church of Christ the King opened 1954. Schools and other institutions: schools for new housing estates: Petteril Bank School (opened in pre-fabricated huts 1943; rebuilt 1972); Inglewood Infant and Junior Schools (opened 1953-4); Pennine Way Primary School (opened 1958); Harraby Secondary School (opened 1956; became North Cumbria Technology College; renamed Richard Rose Academy 2008). Harraby community centre opened 1963. UPPERBY. Acreage: 455 acres [184 ha]. Landownership: see Brisco. Economy: alabaster mill manufacturing plaster of Paris mid-19th century. Clay-digging and brick-making late 19th century. Steam laundry from 1890s to mid-20th century with wadding/dyeing works adjacent c.1900. Major housing development 1920s to 1950s. Places of worship: St John’s church built 1843; chancel added 1889-90; municipal cemetery adjacent from 1881. Primitive Methodist chapel built 1901; still in use. Schools and other institutions: school built c. 1828; rebuilt and enlarged 1854; became parish room when new school built 1912; now Upperby Primary School. Institute, Lamb Street, built 1922. Upperby Park, on former brick fields, opened 1923. Petteril Bank (villa built 1829) extended to accommodate Cumbria Archive Centre, opened 2011.
The Place-name St. Cuthbert Without
Placenames -sources of information
St. Cuthbert Without - place-name elements and their meanings
St. Cuthbert Without - historical place-name forms
created in 1894 with six townships, the parish has no historical place-name forms

